Household Hazardous Waste
Many common household products are considered hazardous and must be disposed of with care. These products include chemicals used for cleaning, home improvement, car care, and others. These products can cause harm to the environment and human health if not disposed of properly. These products should never be poured down a drain, flushed down a toilet, or poured into a storm drain.
For a map of Household Hazardous Waste disposal facilities in California and tips for proper identification, management, and disposal, visit the California Department of Toxic Substance Control Household Hazardous Waste webpage.
Questions? Contact your local wastewater agency using the map below.

Demolition
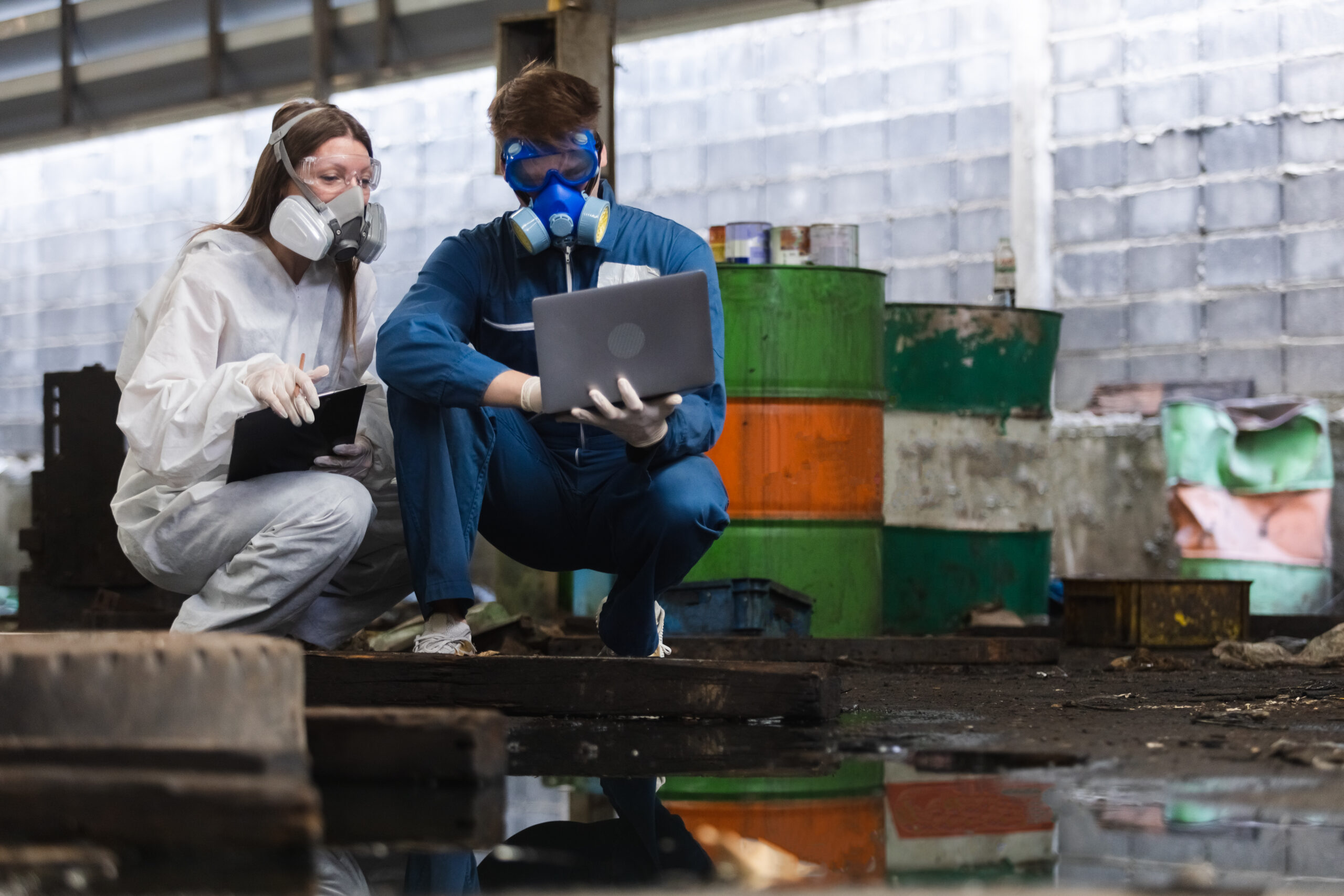
Ready to demolish a building? Before you start, find, remove, and safely dispose of all hazardous materials.
Step 1: Inspect!
Prior to demolition, ALWAYS inspect a structure for hazardous materials. A trained professional should inspect any pre-1980s structure (including residential), as well as medical, dental, veterinary, laboratory, vehicle service, industrial buildings, and other buildings where occupants may have left behind hazardous materials.
Step 2: Protect!
During removal, protect building residents and demolition staff. Segregate hazardous wastes from other construction debris. Consider hiring a professional to segregate the waste. Take precautions, using personal protective equipment and following material-specific guidelines, to protect yourself, building residents, neighbors, and workers from contaminated dust and other potentially harmful releases. Store hazardous wastes in closed containers with proper labeling and secondary containment, if required.
Step 3: Dispose!
Dispose of wastes according to law, to limit liability and protect the environment. Depending on the substance, you may need to dispose of the material in accordance with state and federal hazardous waste disposal laws. If hazardous materials are simply disposed of with other construction debris, they can be released into the environment at the construction site, during transit, or even eventually from the landfill site. Willful or negligent violation of hazardous waste laws can result in civil or criminal penalties.

Generators of Very Small Quantities
If the amount of hazardous waste being generated by a contractor or property management firm is 27 liquid gallons or 220 solid pounds or less, it may qualify as “conditionally-exempt.” Contractors and property management firms would then qualify to use Conditionally-Exempt Small Quantity Generator (CESQG) Programs for disposal. CESQG Programs are operated in conjunction with Household Hazardous Waste Programs.
For help identifying building materials that may be considered hazardous, see additional resources below.