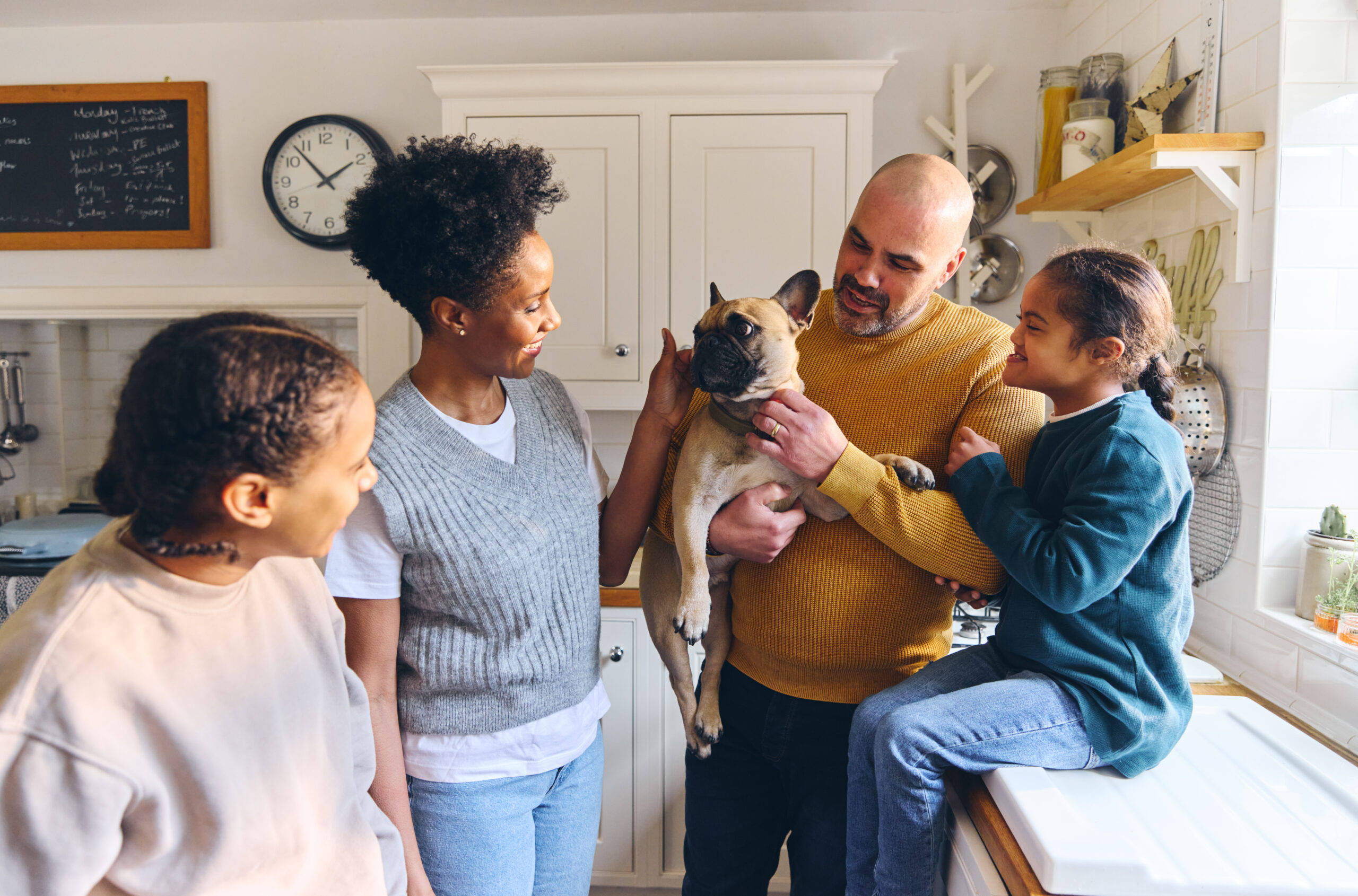
If you are a pet owner or someone who works with pets, you know how important it is to keep our furry friends free of fleas and ticks. However, you may not know that products used to treat fleas and ticks – such as spot-on treatments, collars, sprays, and foggers – expose your family and home to toxic pesticides.
Ask your vet if chewable flea and tick medications are an option for your pet
The California Department of Pesticide Regulation (DPR) reviewed the use of fipronil (a common ingredient in pet/carpet sprays and on-pet topical treatments) and found a potential human health risk to adults and children in households where sprays and topicals are used.[1,2]
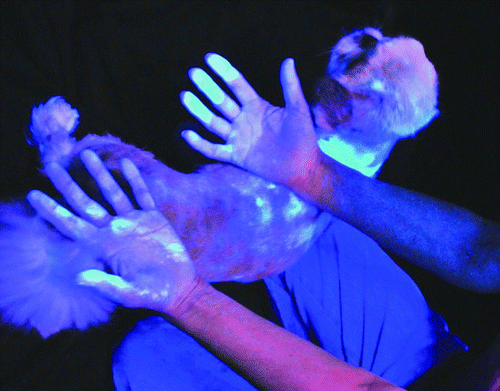
In addition, these pesticides are transferred onto hands, clothing, bedding, and other indoor surfaces. Upon washing, these pesticides make their way into the sewer system. Wastewater treatment processes are not designed to remove these pesticides, leading them to be discharged into San Francisco Bay sometimes at concentrations that are toxic to aquatic species.
To avoid exposing pets, your family, and Bay Area waterways to toxic pesticides from harmful chemicals, use sound flea and tick prevention measures and consider oral medications instead of topical treatments.
Pest management professionals recommend these tips:
Ask your vet if chewable flea and tick products are right for your pet. Not only do oral medications reduce exposure to toxic chemicals, they also may be more effective than topical spot treatments. Chewable products also protect pets against other internal parasites.
If you use topical flea/tick treatments, avoid products that contain fipronil, bifenthrin, imidacloprid, indoxacarb, deltamethrin, or permethrin.
To Prevent Fleas
- Clean your home regularly and thoroughly to prevent flea problems before they start: vacuum carpets, floors, furniture, and inside cracks. Wash pet and human bedding and that pets touch regularly.
- Avoid indoor flea treatments such as house sprays, foggers, and house “bombs.” These items have limited effectiveness, leave a residue in your home, and expose your family to toxic pesticides.
- Use flea combs. Dip the comb frequently into soapy water to capture and drown fleas.
- Use flea traps to determine the size and location of the infestation.
- Visit OurWaterOurWorld.org for more tips about how to prevent and control fleas around your home.
To Prevent Ticks
- If possible, keep your dog’s coat short.
- Try to keep your dog out of grassy areas. Walk in the center of trails and use shorter leashes when walking in the woods.
- Thoroughly inspect your pet after walks before ticks have time to attach. Pay particular attention to the nose, mouth, eyes, ears (inside too), around tails, and under the collar. Inspect yourself and your gear as well.
- Create a tick-free zone in your yard by controlling bushes or tall grass and provide a 3-foot barrier-gap (e.g., wood chips or gravel) between lawns and wooded areas. Keep play and deck equipment away from yard edges. Keep outside areas neat to discourage rodents or other wildlife.
So how do flea and tick products reach the Bay?
Harmful pesticides from these treatments can end up in our local waterways when you do the following:
- Bathe a pet which has been treated with topical tick and flea products: Contrary to manufacturer labels, spot-on products do wash off during bathing. These pesticides wash off your pet and are discharged directly into our wastewater system.
- Wash items that come into contact with a treated pet: Scientific studies indicate that chemicals from indoor flea control (including spot-ons, collars, sprays, and foggers) can wipe off on your hands, clothing, and furniture and travel throughout your home – as shown in the image above.
- Apply outdoor flea and tick sprays: Chemicals from outdoor flea and tick sprays get washed away by storm runoff into our storm drains. This chemical-laced water then flows directly into local waterways without ever passing through a water treatment facility.
Find guidance for veterinarians here.
References
- All DPR fipronil risk assessment documents are available at http://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/whs/active_ingredient/fipronil.htm
- Fipronil Risk Characterization Document, Human Health Assessment Branch, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California Environmental Protection Agency. March 2023. https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/risk/rcd/fipronil_rcd.pdf





